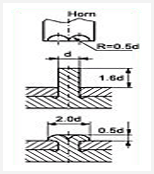
Spin Welding
Spin welding is a process that joins circular thermoplastic parts by bringing the part interfaces together, under pressure, with a circular, spinning motion. One part is held stationary in a fixture, while the other is rotated against it under pressure. The frictional heat that is generated causes the part interfaces to melt and fuse together, creating a strong, hermetic seal.
Spin welding is a process that joins circular thermoplastic parts by bringing the part interfaces together, under pressure, with a circular, spinning motion. One part is held stationary in a fixture, while the other is rotated against it under pressure. The frictional heat that is generated causes the part interfaces to melt and fuse together, creating a strong, hermetic seal.